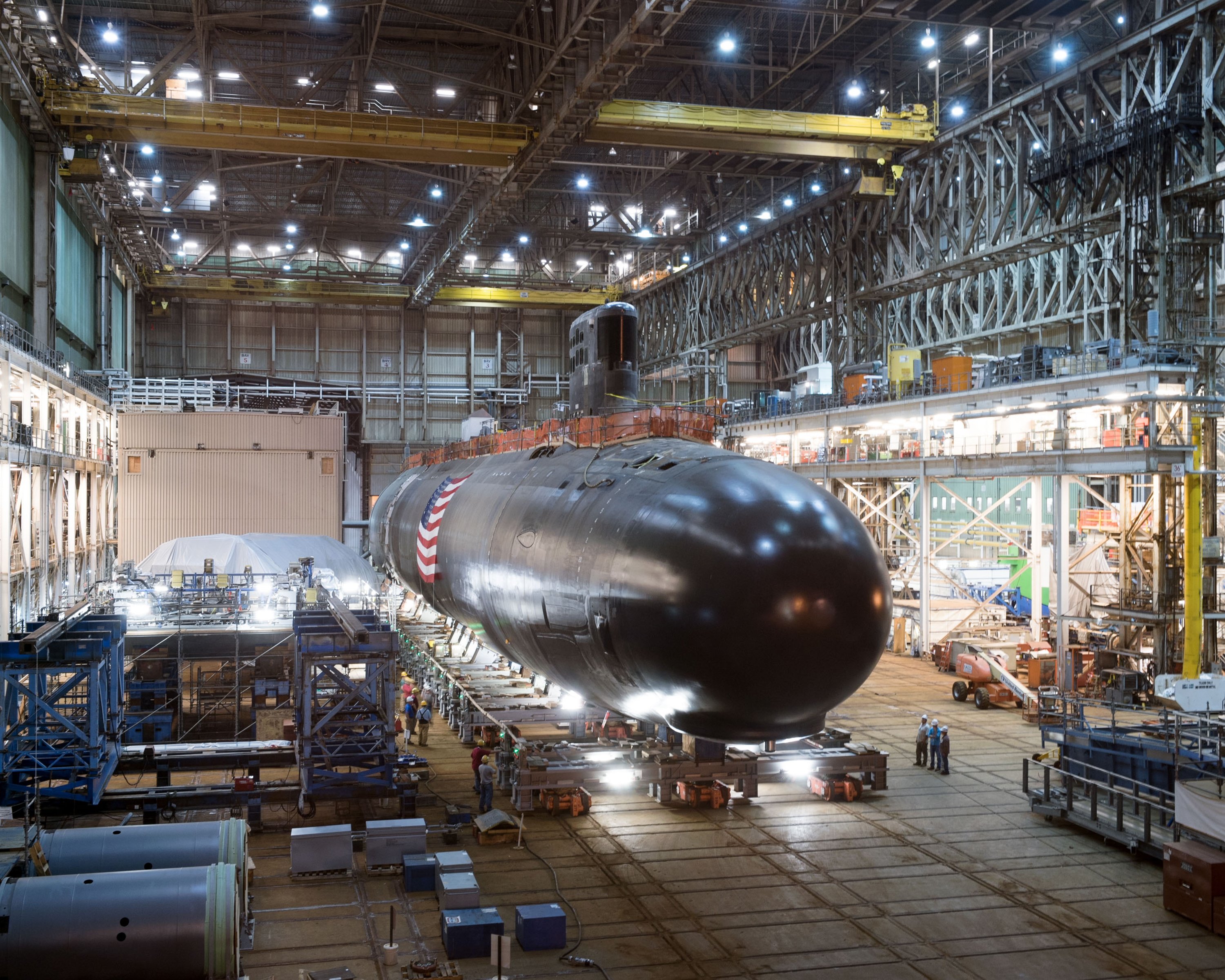
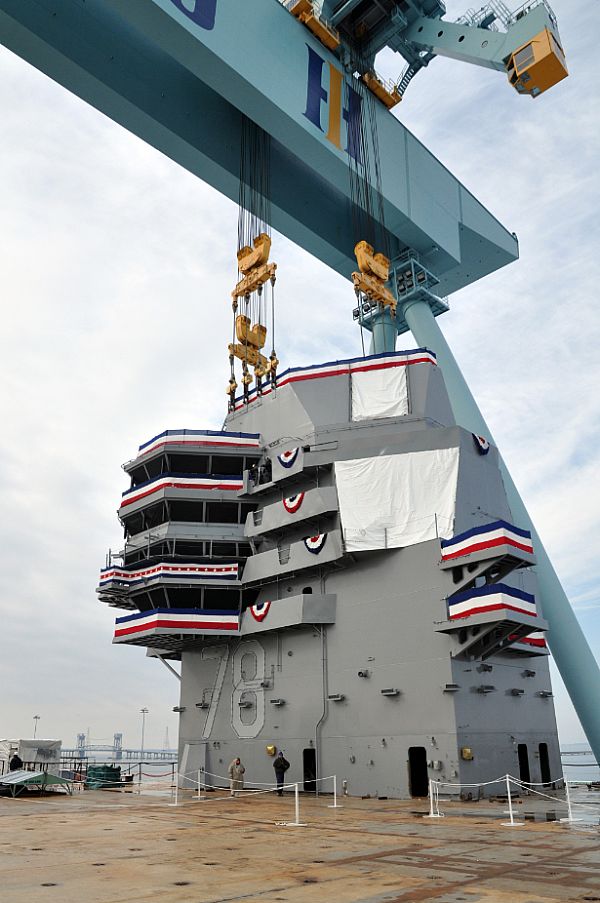
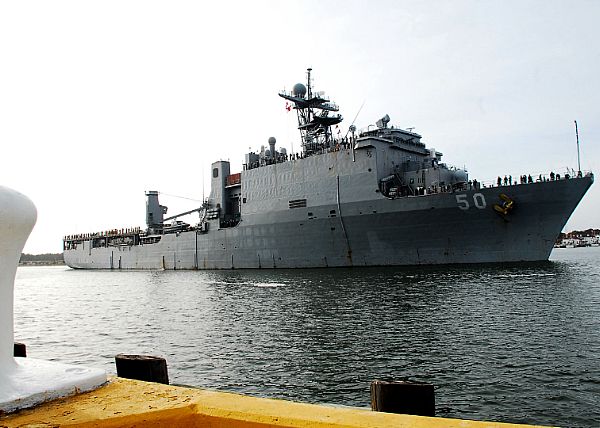
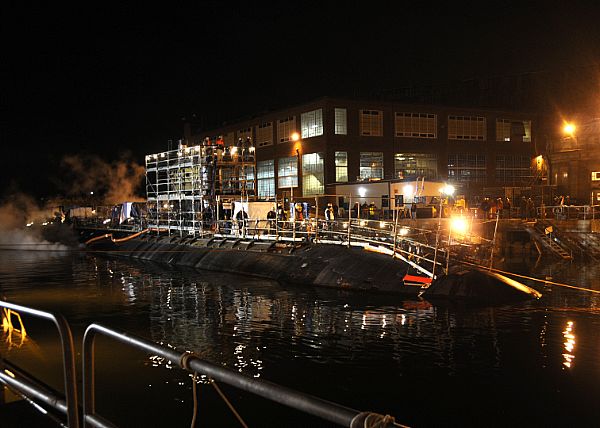
Navy’s Single Sub Buy Plan Raises Concerns with Congress
Lawmakers raised concerns with Navy leaders this week over lags in U.S. naval shipbuilding after the service altered plans for attack boat procurement for the first time in several years.…