U.S. Navy enlisted personnel—unlike those in the other services—wear their jobs on their sleeves. A Marine machine-gunner wears similar collar rank as the rest of his fire team; unless you ask him, or see his military occupation in his file, one could never know his job specifics just by looking at his uniform.
Not so in the Navy.

The Navy’s complicated enlisted system is based on a sailor’s occupation, or rating. Those range from the enduring—quartermaster, yeoman, boatswain’s mate or hospital corpsman—to the more obscure—religious programs specialist, interior communications electrician or legalman.
Each job has its own unique title—such as Boatswain’s Mate 2nd Class Jones—and an insignia denoting the rating included on his or her uniform.
What makes the system so confusing is the constant creation of new jobs, the merging of jobs or eliminating them entirely as the service requires.
For example, in the last several years the Navy has created ratings for unmanned vehicle operators and cyber-warfare technicians while losing or merging jobs such as patternmaker and boiler technician.
The following is a collection of former Navy ratings (and one defunct officer rank) made mostly obsolete by advances in technology and occasionally by more modern stances on race, gender, and—at least in one case—child-labor norms.
Powder Monkey
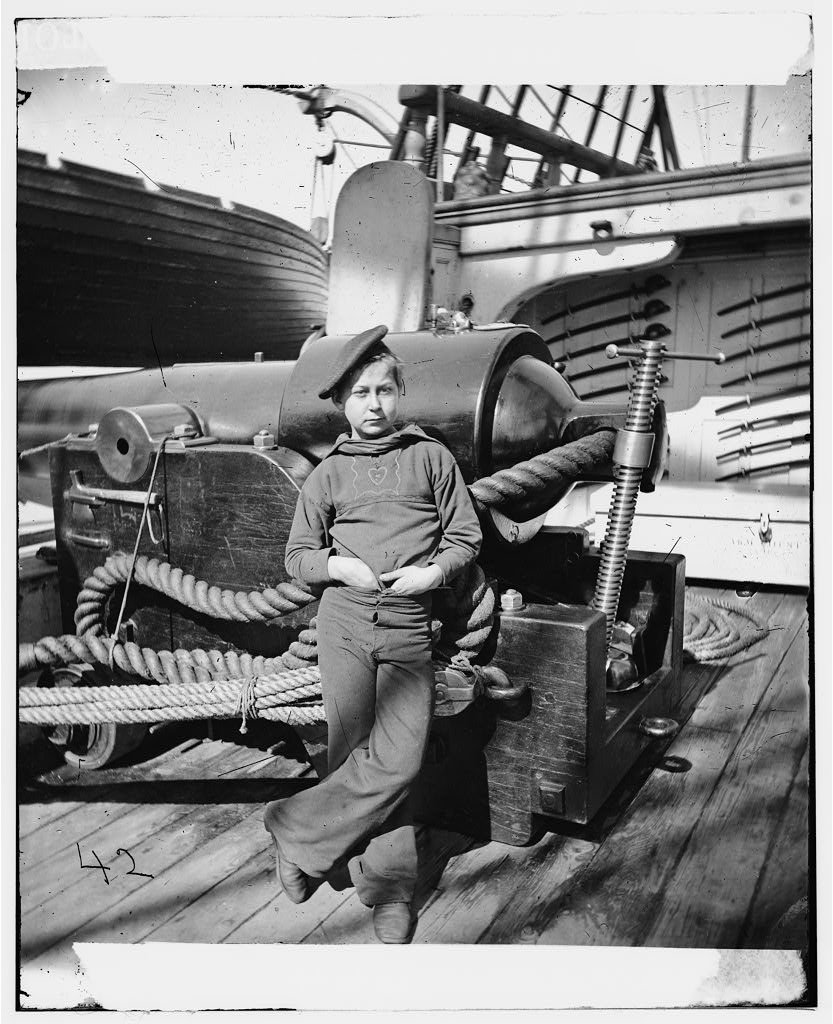

The primary duty of a ship’s powder monkeys was to carry gunpowder from the storage magazine to the crews manning cannons. Regulations in the 19th century did not allow boys younger than 13 to join the Navy (though that was rarely enforced) and children as young as 6 were documented as having served as powder monkeys during the Civil War.
The name most likely comes from the boys’ ability to quickly scamper over and under obstacles on the cramped decks of a ship—like monkeys swinging through trees. They were usually given the rating of Boy, which actually referred to a sailor’s lack of experience at sea rather than his age (many newly recruited adults of slight stature also served as powder monkeys).
The Boy rate was disestablished in 1893 and the Navy became more strict about keeping underage sailors from joining crews. By World War I, shipboard elevators were commonly used to deliver shells to guns.
Chemical Warfareman
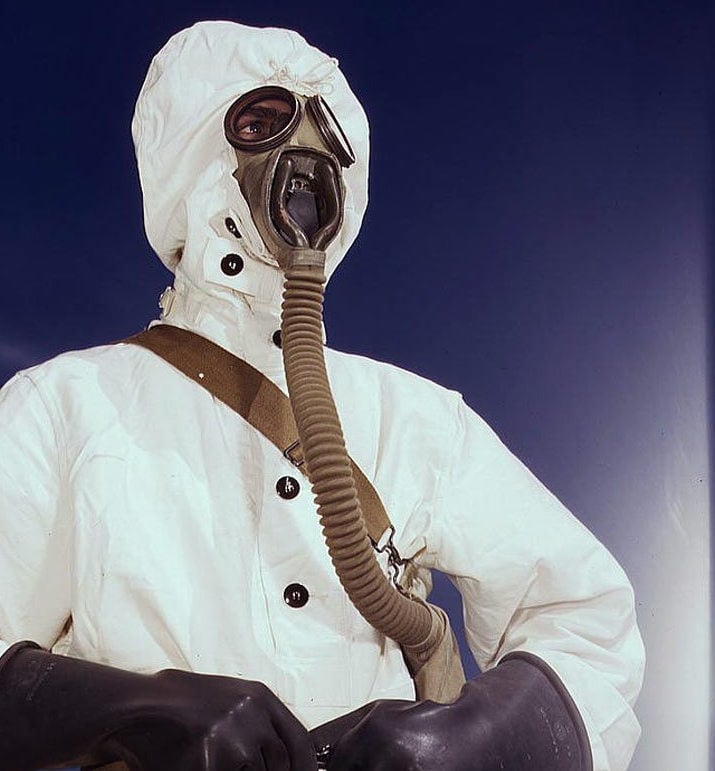

Chemical warfaremen were responsible for damage control in the event of a chemical, biological or radiological attack—not charging into battle with toxic chemicals.
They were trained to repair equipment, initiate decontamination procedures, and administer first aid to gas casualties. The first version of this rating was established in 1942 because of fears that the Japanese and Germans held large stockpiles of weaponized chemical agents. The rating was further refined after the war and existed until 1954, when the duties were consolidated and assigned to the rating of damage controlman.
Loblolly Boy
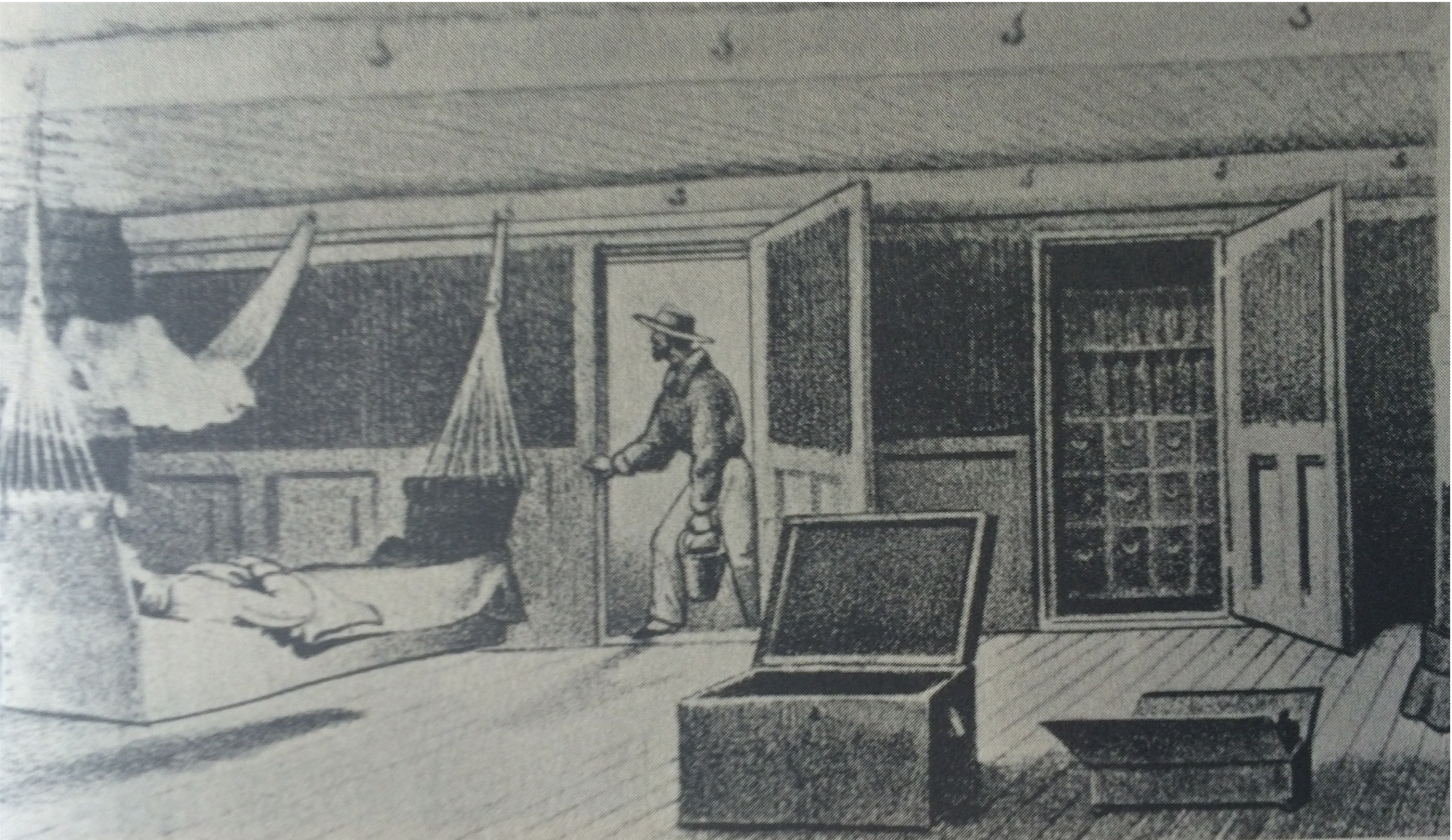

In the late 18th century, U.S. Navy ship crews usually included loblolly boys, young men who had the grim task of assisting surgeons by collecting amputated limbs, hauling the buckets of tar used to cauterize stumps, and spreading sand to absorb blood.
In a practice adopted from Britain’s Royal Navy, they were also responsible for feeding sick and wounded sailors a thick meat and vegetable porridge known as “loblolly,” which is how they earned their name. (Loblolly was also called by the utterly unappetizing name of “spoon meat.”) Loblolly boys remained until 1861, when the rating went through several name changes before evolving into hospital corpsman.
Schoolmaster

Sailors in the 1800s rarely had a formal education, so many ships carried a schoolmaster who was responsible for instructing the crew in reading, writing and arithmetic. The schoolmaster also taught navigation and the other advanced skills needed to make the men better sailors. A schoolmaster might even try to culturally enrich the crew by exposing it to music and art. However, many captains came to view schoolmasters as ineffective and a waste of ship resources. It was frequently reported that many schoolmasters were lazy and ubiquitously drunk. The Navy decided chaplains had the educational background needed to help enlighten a ship’s crew and the schoolmaster rate was eliminated in 1900.
Admiral of the Navy
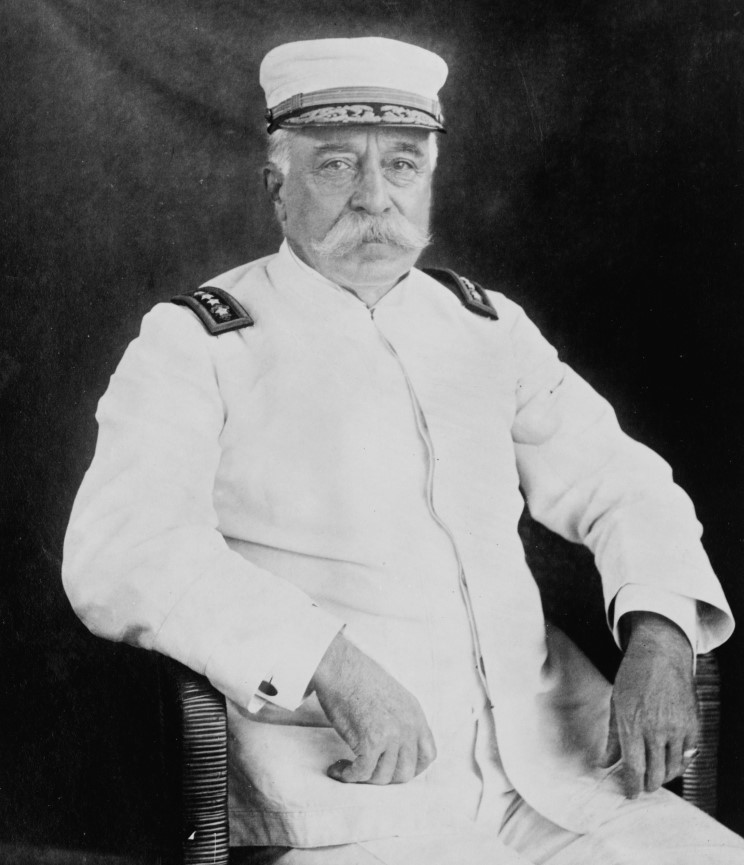

The only exception to enlisted rates in the list is the defunct supreme officer rank of admiral of the Navy. Only one person has been promoted to the six-star equivalent rank: Adm. George Dewey. Dewey returned from his 1898 victory at the Battle of Manila Bay to a hero’s welcome and was so popular that products ranging from dishware to clocks bearing his image could be found in homes throughout the country. In addition to being promoted to the unprecedented rank of Admiral of the Navy, he was also encouraged to make a run for the White House (but lost support when he began to warn that the United States would one day be at war with Germany). When the five-star rank of fleet admiral was established in 1944, it was determined that Dewey’s rank of admiral of the Navy was equivalent to six stars.
Incidentally, two men have been made general of the armies—General John “Black Jack” Pershing (following WWI) and General George Washington (though he had been dead for 177 years when he received the promotion).
Pigeon Trainer
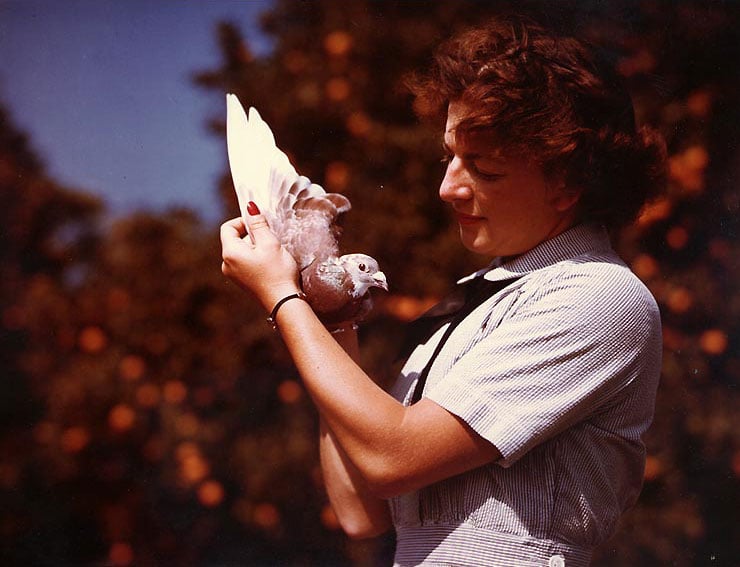

The Navy began to use “pigeoneers” at the dawn of the 20th century, tasking them with the feeding and caring of the flocks of birds used to deliver messages. In addition to their natural homing abilities, pigeons were valued because they could quickly carry messages over long distances at high altitude. The development of radio soon brought more efficient forms of communication, but the Navy continued to include pigeon trainers in the ranks until 1961 to ensure there was an emergency line of communication in periods of radio silence or in the event of some type of technical failure.
Airship Rigger
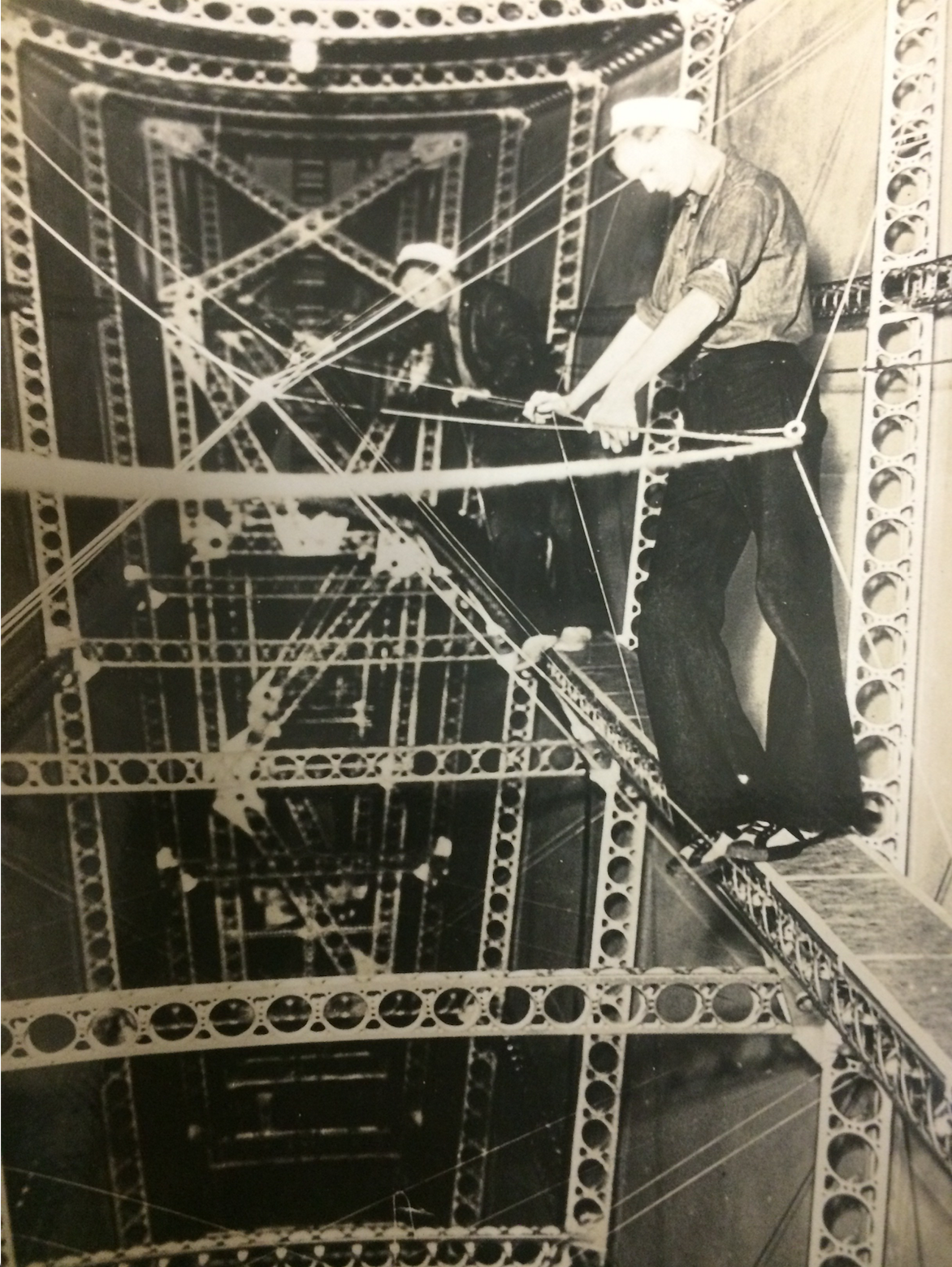

In the 1920s the Navy began to view airships as platforms that could be used for long-range reconnaissance and antisubmarine warfare. Initial enthusiasm was so high that some analysts believed that airships were the true future of the Navy and that the aircraft carriers being concurrently developed were nothing but an expensive fad.
The airship crews included riggers who were responsible for maintaining the infrastructure of the dirigible and repaired any tears in the gas cells or skin. Used to escort convoys in the Atlantic during World War II, the airships proved to be an effective deterrent to submarine attacks but were superseded by advances in heavier-than-air planes as well as radar and sonar.
The airship rigger rating was disestablished in 1948 and the entire airship program was abandoned in 1961. However, airships were resurrected in 2011 when the Navy again began to experiment with them as surveillance platforms.
International Business Machine (IBM) Operator
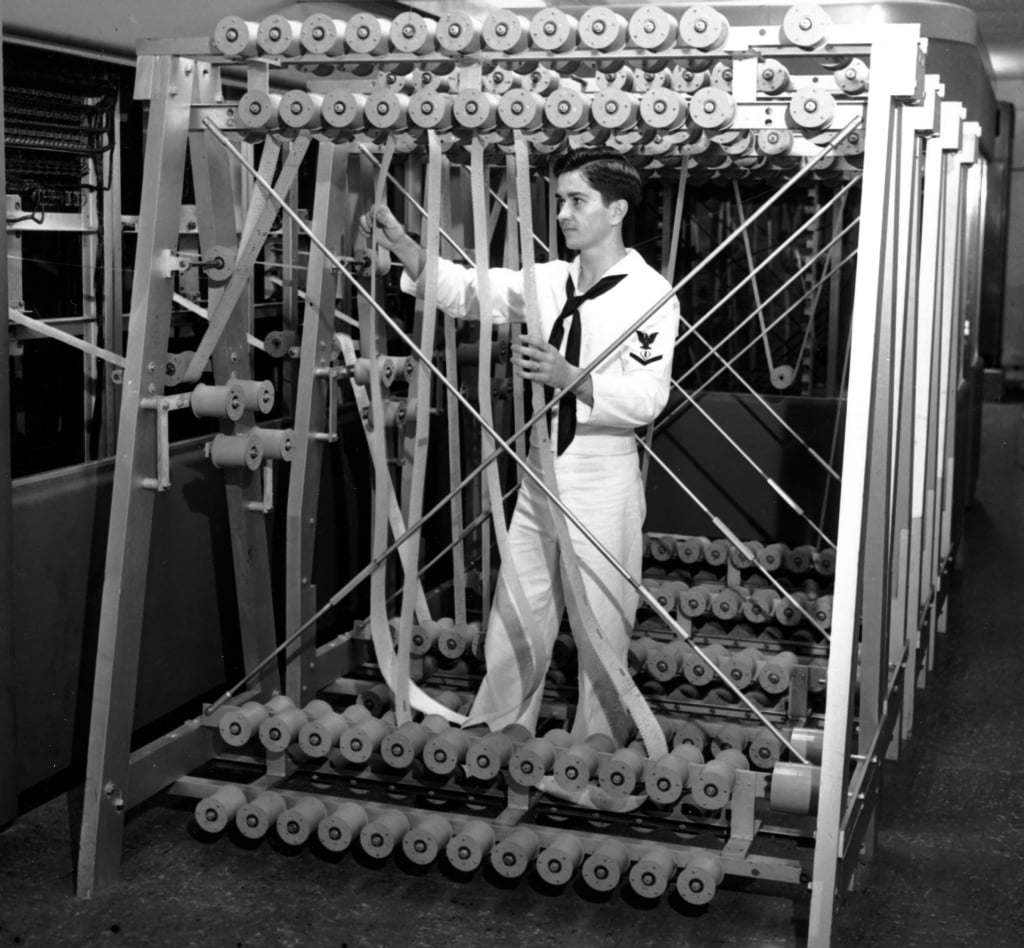 With a need to better calculate gun trajectories, ensure accurate accounting, and handle mass logistics, the Navy turned to IBM tabulating equipment during WWII. The move gave birth to the rating of International Business Machine operator. The rating only existed for about a year before it was it changed to the generic but even more unwieldy name of punched-card accounting machine operator, but IBM continued to develop new products for the Navy. In 1944, IBM introduced the nation’s first large-scale electromechanical calculator (the automated sequence controlled calculator or the “Harvard Mark I”) that was used by the U.S. Navy Bureau of Ships. The operator rating went through several transformations until becoming the current information systems technician.
With a need to better calculate gun trajectories, ensure accurate accounting, and handle mass logistics, the Navy turned to IBM tabulating equipment during WWII. The move gave birth to the rating of International Business Machine operator. The rating only existed for about a year before it was it changed to the generic but even more unwieldy name of punched-card accounting machine operator, but IBM continued to develop new products for the Navy. In 1944, IBM introduced the nation’s first large-scale electromechanical calculator (the automated sequence controlled calculator or the “Harvard Mark I”) that was used by the U.S. Navy Bureau of Ships. The operator rating went through several transformations until becoming the current information systems technician.
Jack of the Dust
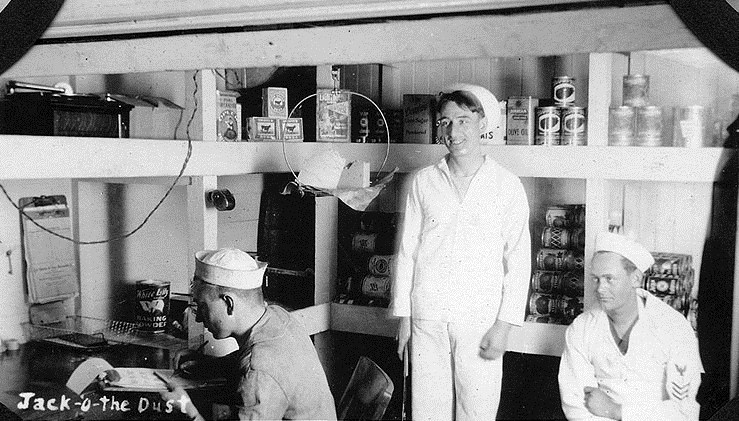

In another holdover from the Royal Navy, the sailor who assisted the cook by breaking out provisions was known as Dusty, or Jack of the Dust, because he was often covered in flour from working in a bread room. The rating was established in the U.S. Navy in 1876 and referred to the storeroom keeper. Jack of the dust ceased being an official rating in 1893, but the name lives on in the modern Navy as an informal title given to the culinary specialist in charge of canned goods or the sailors assigned to food-service duty.
Aviation Carpenter’s Mate

Early U.S. Navy planes were fairly delicate machines built of wood and canvas. With shipboard aviation operations still in their infancy, the planes were often placed in less than optimum flying and storage conditionsl, which resulted in damage to the wooden frames, struts and props. Recognizing that they needed sailors skilled with a lathe to repair the damaged planes, the Navy established the aviation carpenter’s mate rating in 1921. Advances in aviation and the development of all-metal planes in the mid-1930s began to diminish the call for aviation carpenters. The rating was disestablished in 1941 and the duties were absorbed by the aviation metalsmith—the forerunner of the current aviation structural mechanic.
Coal Heaver
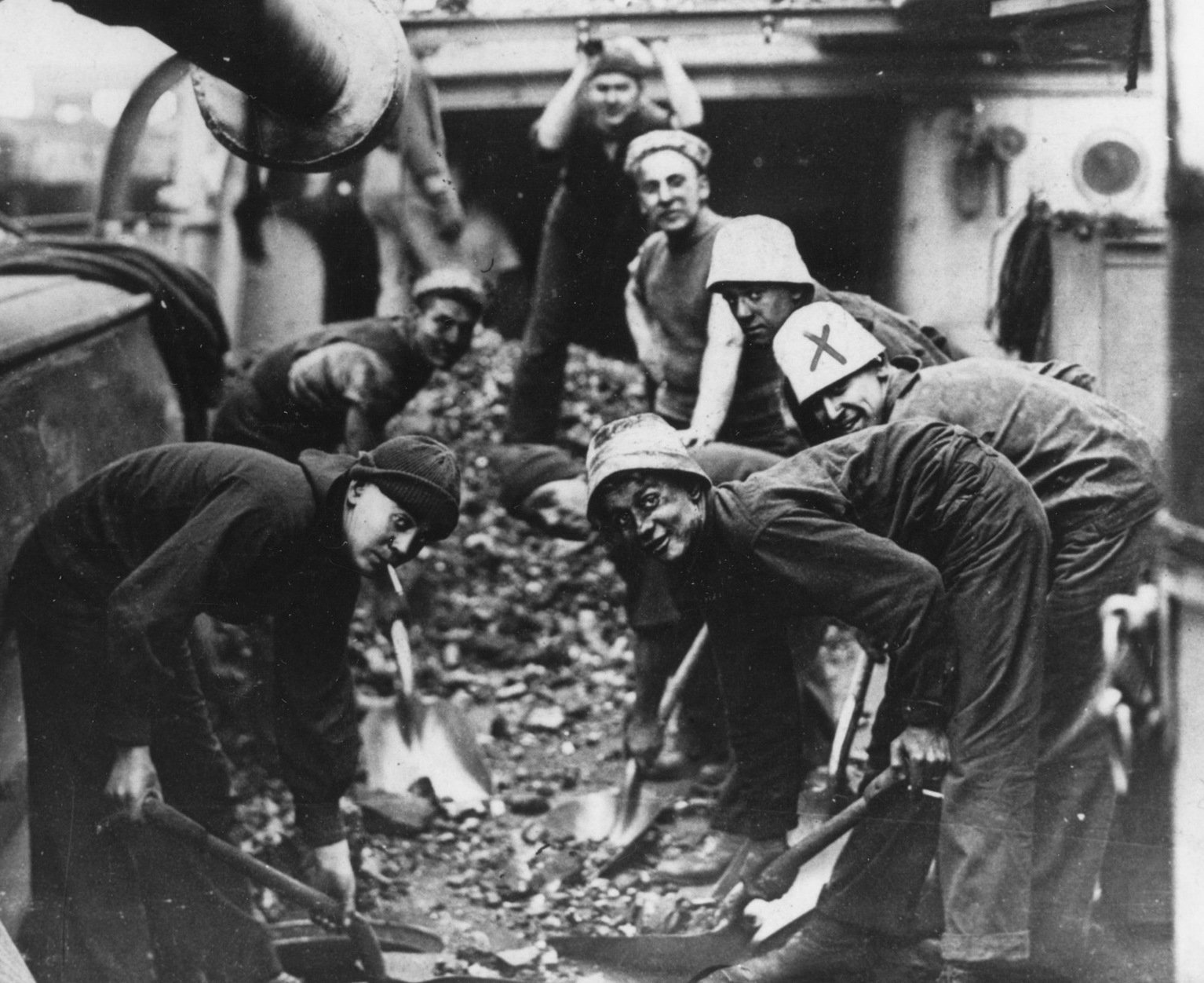

As the age of sail gave way to the age of steam, ships began to require coal.
Tons upon tons of coal.
Coal heavers came into service in 1842 and hauled coal from a ship’s bunker to the boiler furnaces. A coal heaver could make up to 50 trips a day with a full bucket weighing about 140 pounds. Since it was hot, dirty and dangerous work, the members of the “black gang” received substantially higher pay than other sailors. In 1893, the rating was changed to the less strenuous sounding (but probably equally backbreaking and dirty) coal passer. The duties were incorporated into the rating of fire 3c in 1917.
Steward (Filipino)
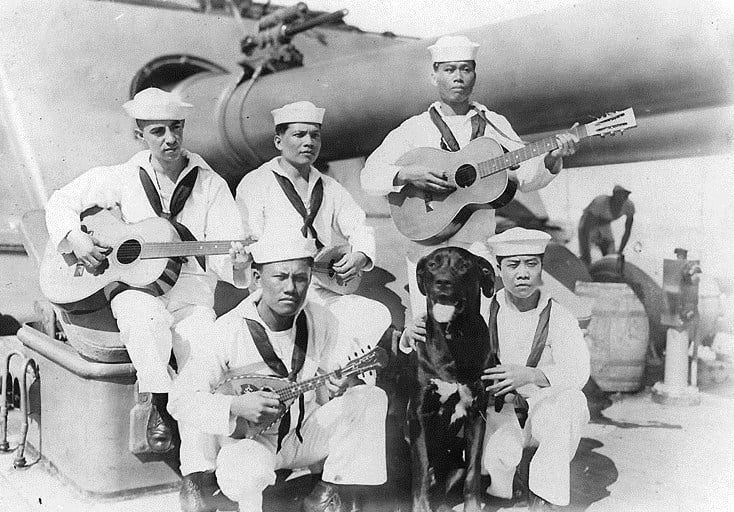

With the defeat of Spanish forces 1898, the U.S. took possession of the Philippines and soon began to recruit Filipinos to serve in the Navy. For the next 70 years, Filipinos were permitted to join the Navy without U.S. citizenship but were largely restricted to the steward rating and assigned to work in galleys and wardrooms.
At the peak of the program, there were more Philippine nationals in the U.S. Navy than the Philippine navy. It was not until 1971 that the policy was changed to allow Filipinos to enlist in the Navy and enter any rating for which they were considered qualified through education or experience. When the U.S.-Philippine Military Bases Agreement expired in 1992, the program allowing Philippine nationals to serve in the U.S. Navy was also terminated.
Ship Cooper
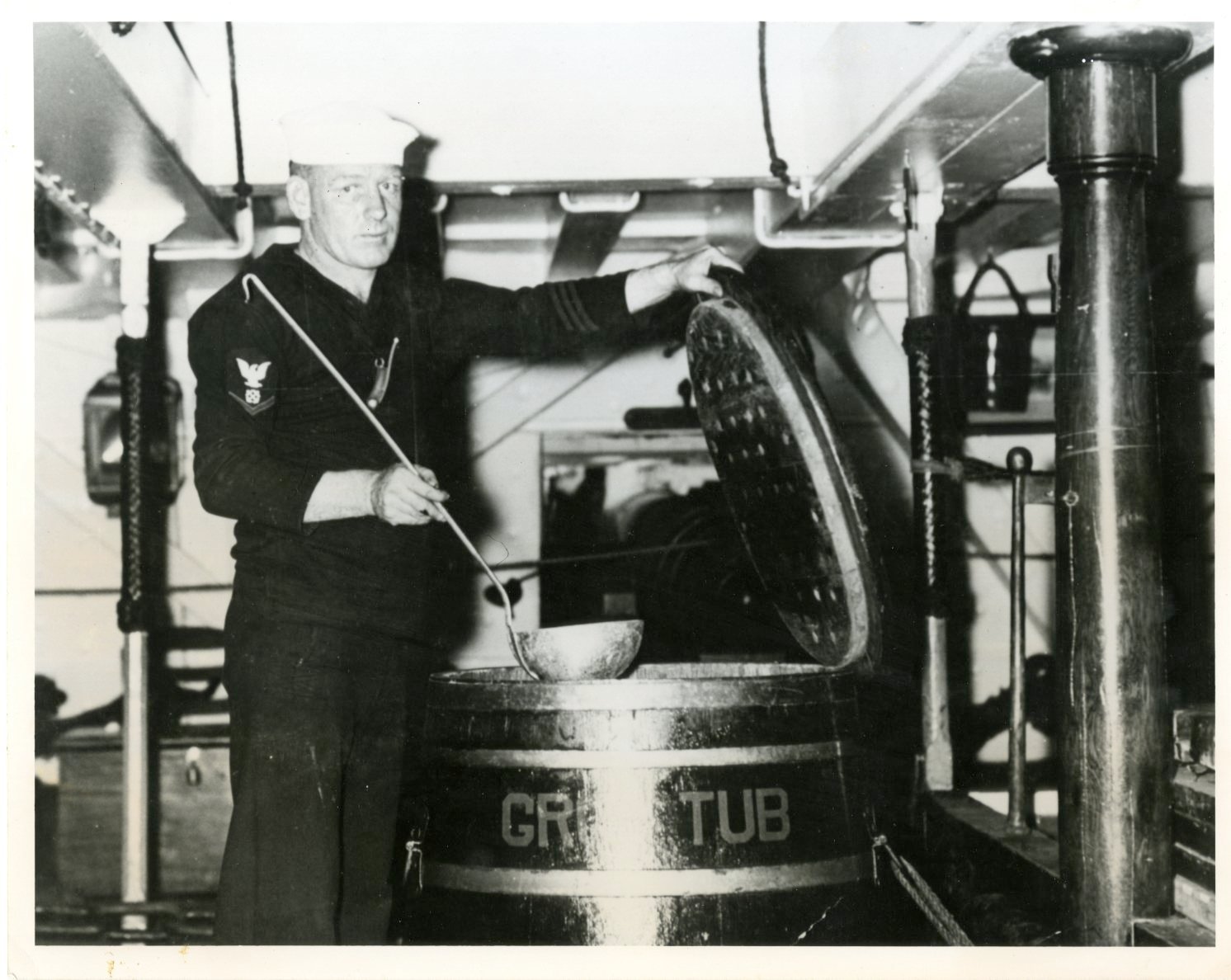

The ship cooper made and repaired barrels, casks, and buckets, which were essential at sea. Well-constructed wooden containers were used not only to transport and protect food, water, and gunpowder, they held the crew’s morale-boosting rum rations (at least until the Navy banned alcohol on ships). Coopers remained until 1884 when more durable material such as steel began to replace wood, but their legacy survives in the term “scuttlebutt.” Coopers would take a wooden butt (a type of cask) and scuttle it by punching a hole to provide the crew with drinking water. The crew would swap gossip while gathered at the cask on breaks (just like modern water-cooler conversations)—which is why many old salts still refer to news and rumors as “scuttlebutt.”