The People’s Liberation Army is building a South China Sea helicopter base that could be a key node in a Chinese anti-submarine warfare (ASW) network across the region, according to new satellite images and analysis shared with USNI News on Friday.
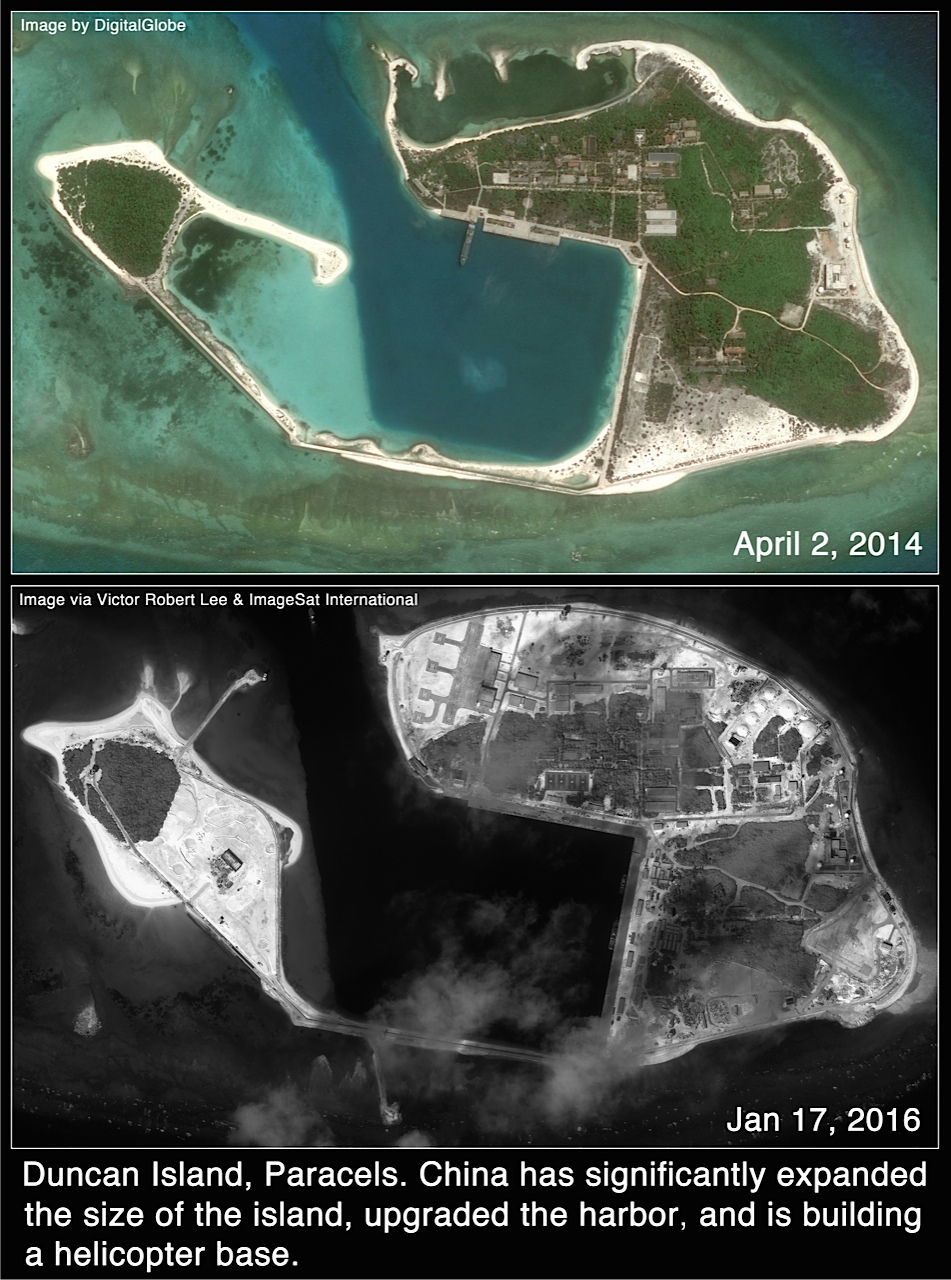
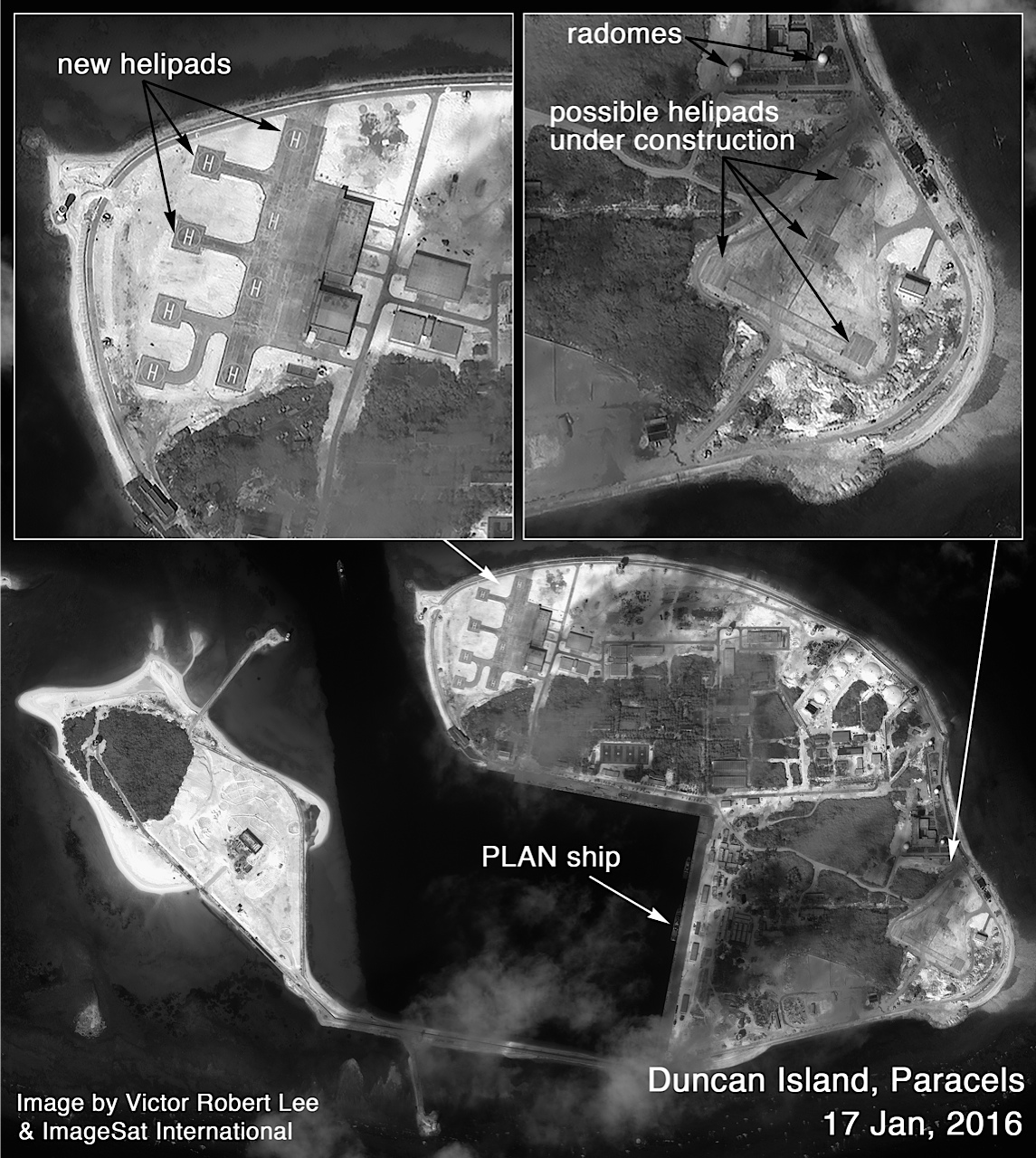
The imagery — first published on news site The Diplomat — show what appears to be extensive reclamation work to build could easily be an ASW helicopter base on Duncan Island, about 200 miles from the coast of Vietnam in the disputed Paracel Islands.
The base “could signal a step-up in China’s ASW capabilities across the South China Sea. A network of helicopter bases and refueling stops scattered across the South China Sea, using no more than the bases China is already known to be building, would make almost any coordinate in the sea reachable,” read the analysis by Victor Robert Lee.
“By hopscotching between bases, the [ASW] helicopter fleet would be unconstrained by fuel range or limited numbers of ship-borne landing berths, creating a continuous and contiguous web of surveillance and response capability.”
 The analysis went on to say “such a web would have utility beyond anti-submarine warfare, and would probably reshape surface ship and aerial combat strategies in the region,” Lee wrote.
The analysis went on to say “such a web would have utility beyond anti-submarine warfare, and would probably reshape surface ship and aerial combat strategies in the region,” Lee wrote.
In reaction to the revelation, Pentagon officials reiterated their call for all South China Sea nations to island reclamation work, in a Sunday statement to USNI News
“The United Sates continues to call on all claimants to halt land reclamation, construction and militarization of features in the South China Sea,” spokesman Cmdr. Bill Urban told USNI News. “While the United States does not take a position on sovereignty claims to land features, we have growing concerns about China’s pattern of assertive behavior, which creates uncertainties about China’s strategic intentions.”
Naval analyst Eric Wertheim told USNI News last week, if the analysis holds up, it would give the Chinese more military options regionally.
“If it turns out to be true. It’s another example of China exercising its effort to control the South China Sea,” the author of the U.S. Naval Institute’s Combat Fleets of the World said.
“From a military perspective it certainly has an impact as these bases can serve as unsinkable aircraft carriers.”
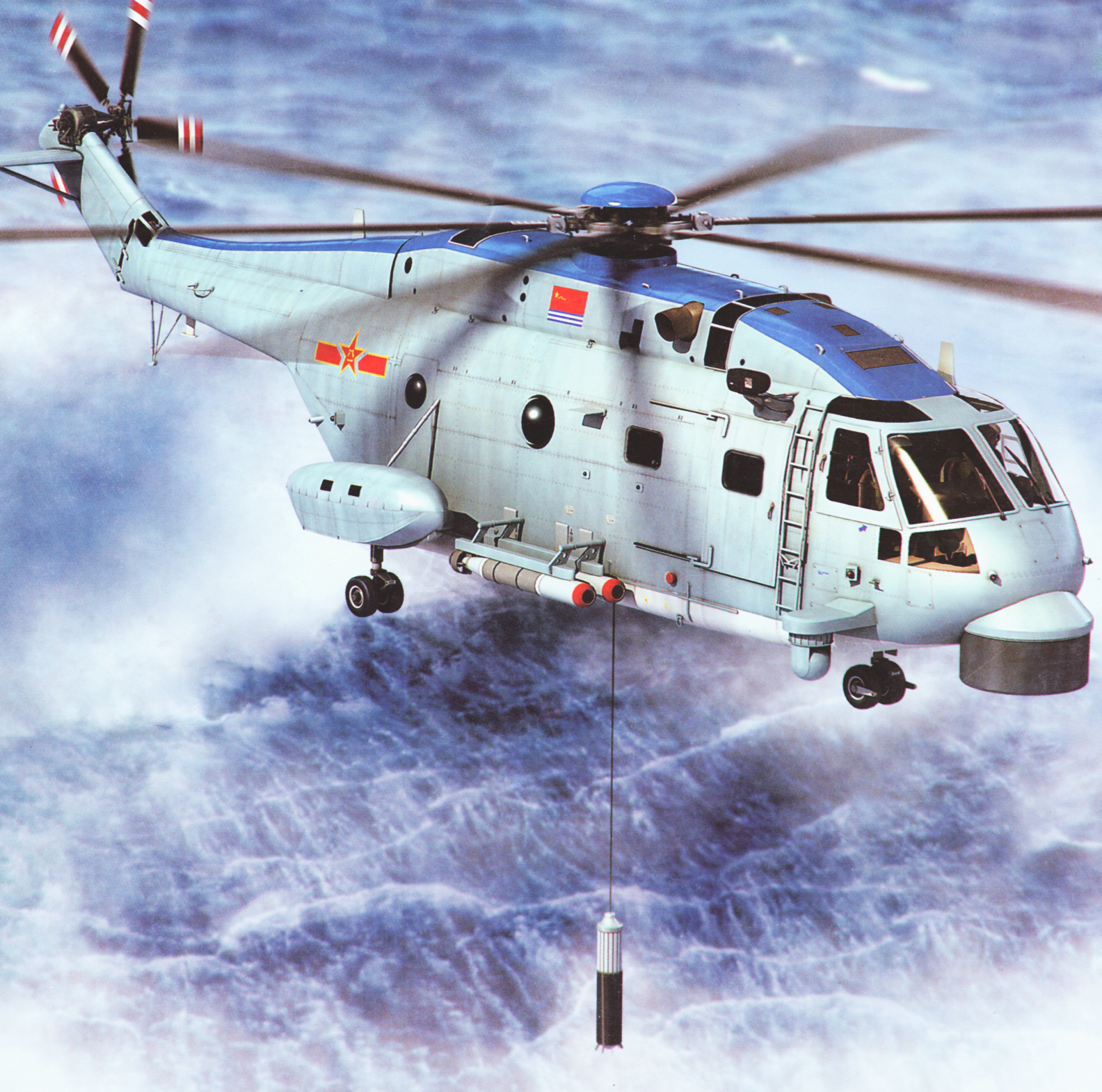
According to Wertheim, the bases could sustain and act as lily pads for the PLAN’s new Changhe Z-18F ASW variant – based on the French SA 321 Super Frelon heavy lift helicopter – which have a range of 450 nautical miles. The Duncan Island installation would put the helicopters easily in range of Vietnam’s maritime territory.
 In September, Pacific Command commander Adm. Harry Harris told the Senate how he viewed the expanded installations across the entire region.
In September, Pacific Command commander Adm. Harry Harris told the Senate how he viewed the expanded installations across the entire region.
“If you look at all of these facilities — and you could imagine a network of missiles sites, runways for their fifth generation fighters and surveillance sites and all that — it creates a mechanism in which China would have de facto control over the South China Sea in any scenario short of war,” Harris said.
“These are obviously easy targets in war, it’s what we call in the military, “grapes” if you will, but short of that, the militarization of these features pose a threat against all other countries in the region.”
News of the base comes as Vietnam is in the midst of modernizing its submarine force to include six Russian-built improved Kilo-class diesel electric attack submarines. The submarines, acquired for the maritime defense of Vietnam’s substantial coastline, are part of a Hanoi naval expansion that would assert Vietnam claims in the region.
The disparity between the Vietnamese Navy and the PLAN and China’s heavily armed coast guard ships, was highlighted in 2014. That May, China sent a $1 billion offshore oil platform inside Vietnam’s disputed economic exclusion zone (EEZ) and had ringed it with ships to prevent challenges. If China, for example, made a similar attempt in the future, it could make it riskier for Vietnams reconstituted submarine force to intercede with closer ASW helicopters.
While the reclamation work in the Paracels – where last month the U.S. sent the guided missile destroyer USS Curtis Wilbur (DDG-54) on a freedom of navigation operation – is not as controversial as the ongoing work the Chinese have done to build artificial islands in the Spratly Islands near the Philippines.
In the last two years China has turned low tide elevations into military-style installations – though China insists they aren’t for military use.
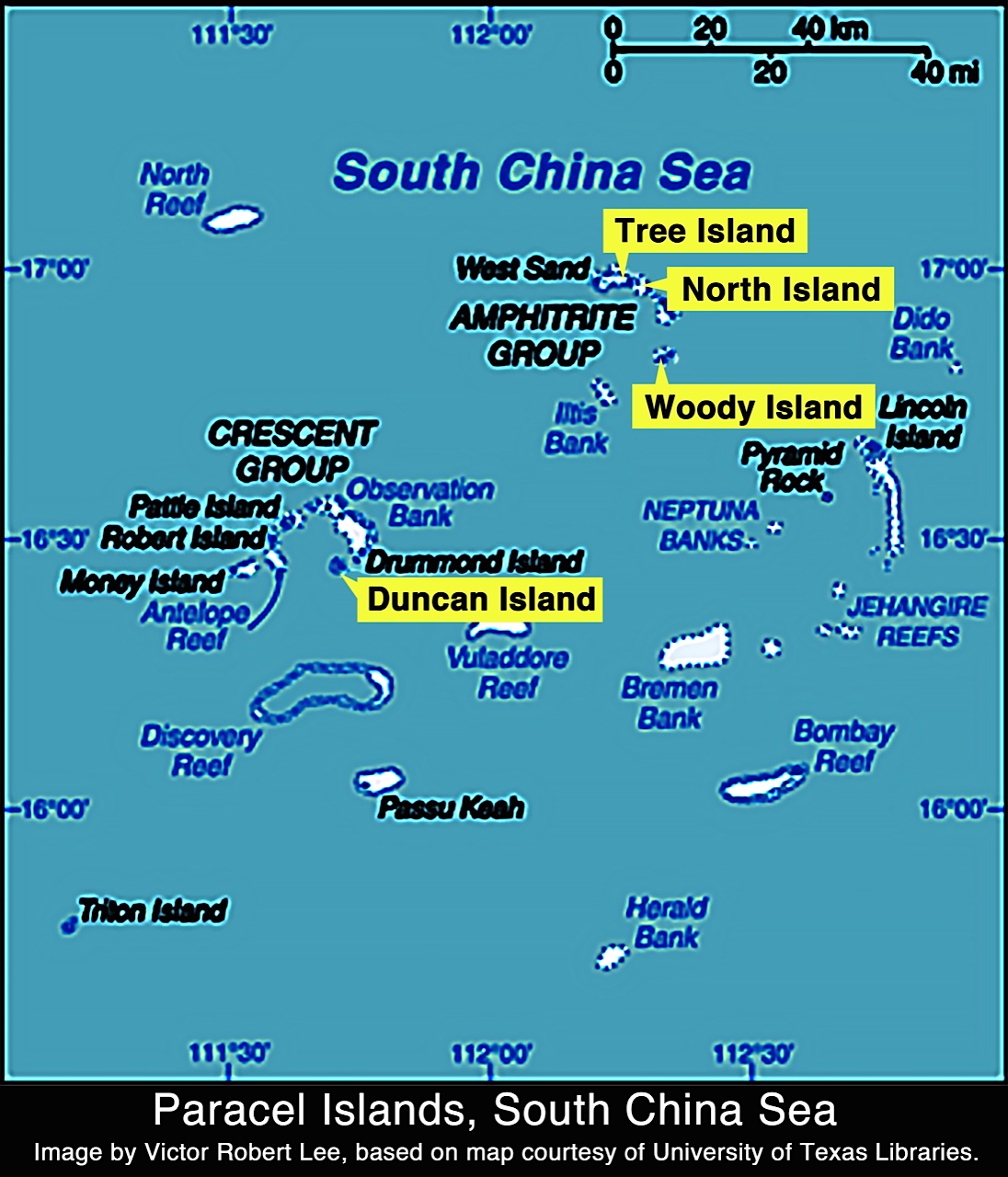 The Chinese controlled territories in the Paracels – on the other hand – are recognized land features that China has controlled since the mid-1970s while Vietnam and Taiwan also have claims.
The Chinese controlled territories in the Paracels – on the other hand – are recognized land features that China has controlled since the mid-1970s while Vietnam and Taiwan also have claims.
In addition expanding the territory on Duncan Island by more than 50 percent in the last year, China has also expanded its Paracel holdings at its airbase at Woody Island, North Island and Tree Island.
“The recent developments at Tree, North, and Duncan islands indicate that Beijing is augmenting its position in the Paracels, which have been overshadowed of late by China’s epic construction projects in the Spratlys,” Lee wrote.
The changes in progress will in the Paracels “probably reshape surface ship and aerial combat strategies in the region.”





