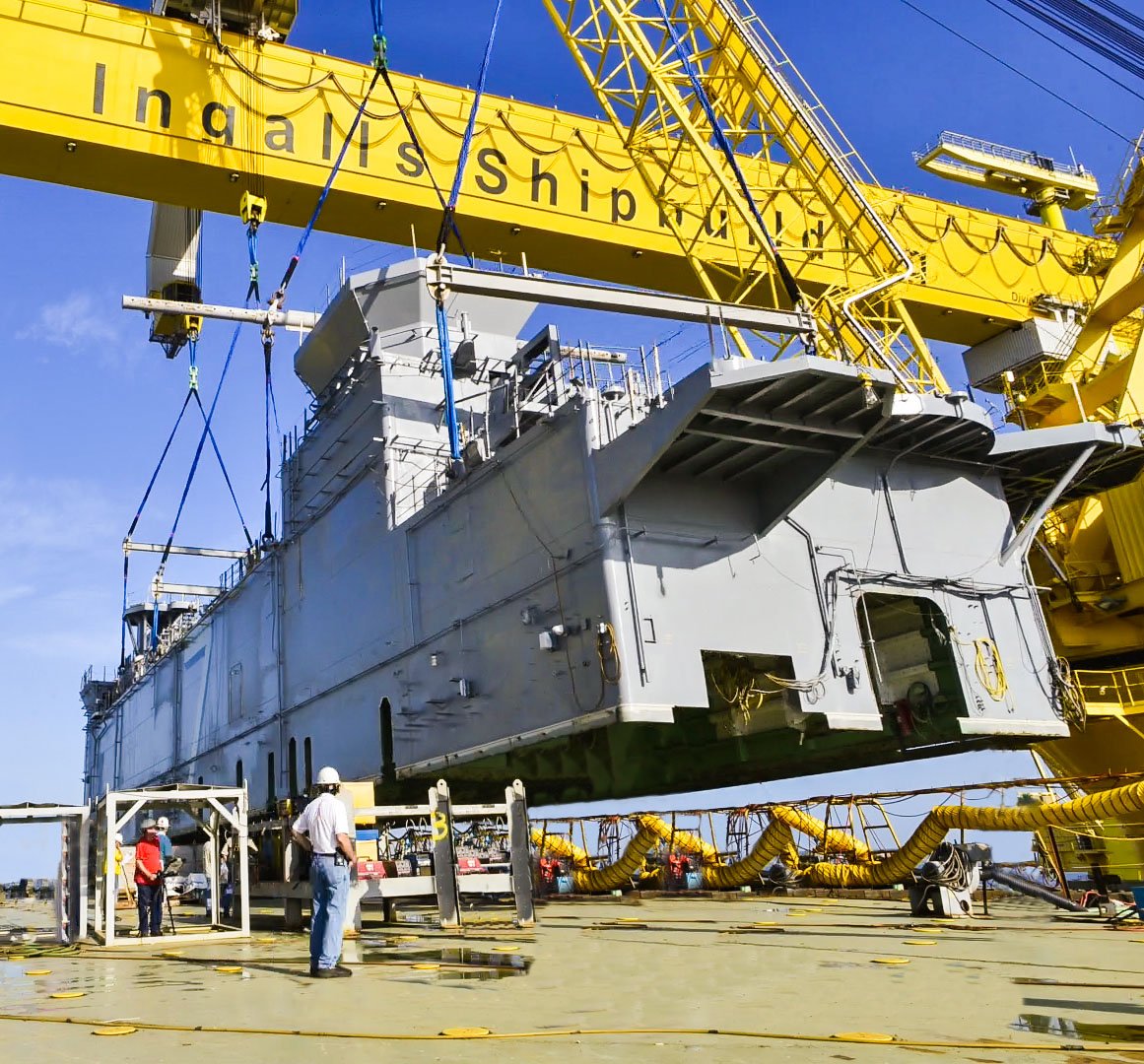
CAPITOL HILL — The Navy and Marine Corps are running up against a deadline to add more amphibious warships to the fleet before older hulls start retiring, Marine Maj. Gen. David Coffman told lawmakers and shipbuilding industry representatives at a congressional forum Tuesday.
Recognizing this is a moment when the Hill is pushing to build more ships faster, Coffman said he’s focused on ensuring these new ships are designed to accommodate changing technologies and remain useful for 50 years.
“We’re trying to make sure we have the full ability to take advantage of a multi-year buy,” Coffman, the director of expeditionary warfare on the chief of naval operations’ staff (OPNAV N95), said.
Coffman was referring to the possibility of the Navy buying 13 San Antonio-class LPD Flight II ships in a block buy contract. These ships are intended to replace Whidbey Island-class LSD ships.

As an example, Coffman cited the need to prepare future ships to handle the networking needs of unmanned and autonomous surface and undersea vehicles, which will be incorporated into the amphibious forces of the future. Unmanned surface and undersea vehicles have the potential to dramatically change the way amphibious forces operate, he said.
“We have a moonshot idea for amphibious assault, which says it’ll be a long time before you see a Marine step off of something because we’re going to go autonomous,” Coffman said. “Get autonomous and unmanned to do a lot of the work.”
Also, incorporating the networking needs of the F-35B Lightning II Joint Strike Fighter into ship design is critical to the Marine Corps ability to use the aircraft, Coffman said. Future amphibious assaults will most likely occur in contested, even urban areas.
Since the Marine Corps is counting on the F-35 playing an important role securing such contested locations, Coffman wants to continually ask what can be done better and how to improve the ship class’ capabilities instead of just settling on a single design.
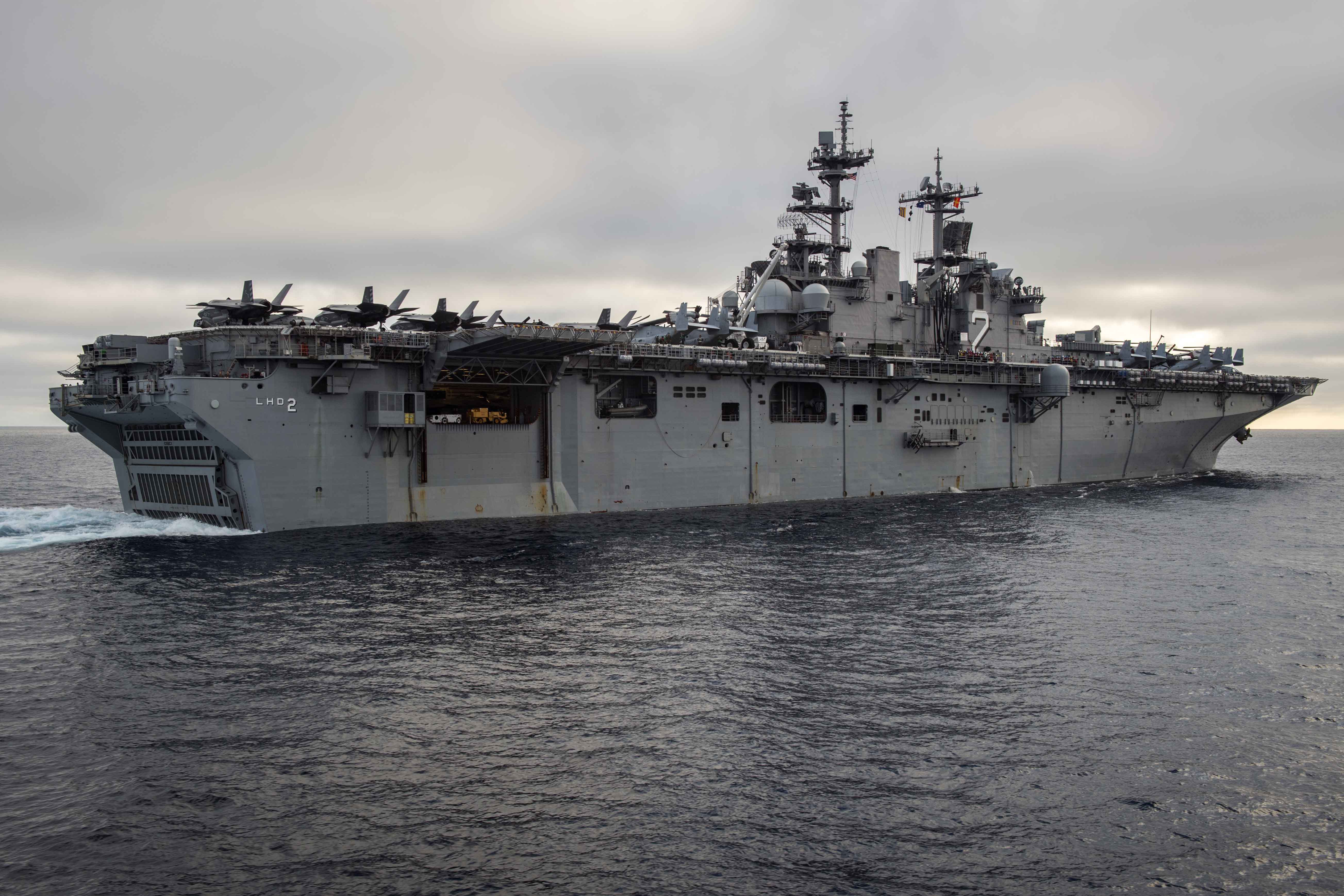

“No one else on the planet can do what we do in the littoral space,” Coffman said.
But the needs of the Navy and Marine Corps to perform in the littoral space currently outpaces the nation’s amphibious warship capacity, said Rep. Rob Wittman (R-Va.). The Navy’s shipbuilding plan, which calls for building a 355-ship fleet, is a good start, but the critical number Wittman said is the 38 amphibious ships included in that plan. Previously, Wittman has criticized the slow pace of the Navy’s shipbuilding plan.
USS Wasp (LHD-1) is expected to reach the end of its anticipated working life by 2030. The concern is older ships such as Wasp will retire before the Navy reaches the goal of 38 amphibious ships, making it nearly impossible for the shipbuilding pace to ever increase the total number of amphibious hulls in use.
“Marines can do almost anything, Wittman said.”But until they can walk on water we better be building them more ships.”