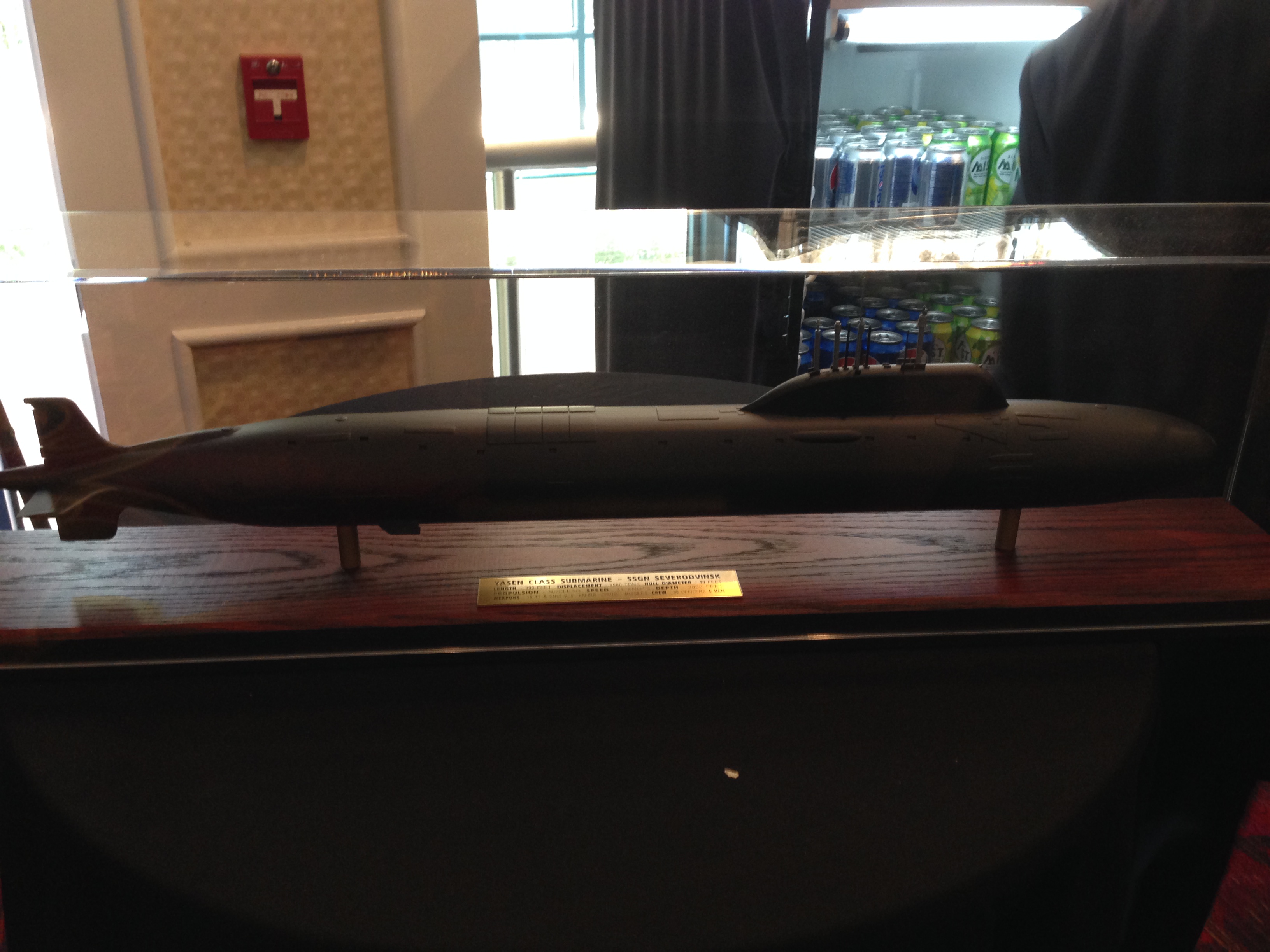
One of the U.S. Navy’s top submarine officers was so impressed with Russia’s new Project 885 nuclear attack boats that he had a model of K-329 Severodvinsk built for his office.
Rear Adm. Dave Johnson, Naval Sea Systems Command’s (NAVSEA) program executive officer (PEO) submarines said he had the model of Severodvinsk placed outside his office in a common area so that he could look at it every day on his way to his office.
“We’ll be facing tough potential opponents. One only has to look at the Severodvinsk, Russia’s version of a [nuclear guided missile submarine] (SSGN). I am so impressed with this ship that I had Carderock build a model from unclassified data.” Johnson said last week during the Naval Submarine League’s symposium in Falls Church, Va.
“The rest of the world’s undersea capability never stands still.”
The Russian attack boat had been in construction since 1993 and only entered sea trials late in 2011. The boat finally became operational earlier this year. A cash-strapped Russian Federation had to repeatedly delay completion of the submarine in the chaos that followed the collapse of the Soviet Union.
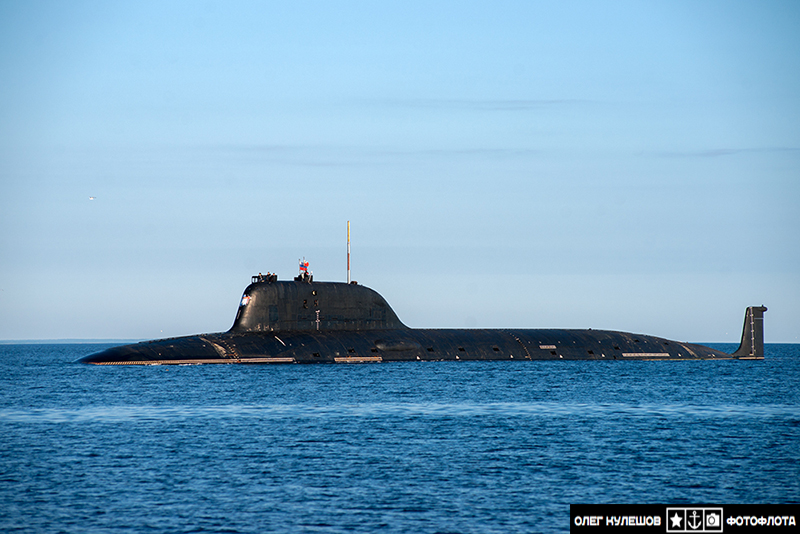
Severodvinsk is the most capable Russian attack submarine ever built and leverages many of the technologies the Soviet Union invested in during the 1970s and 1980s.

The 13,800-ton, 390-foot long, submarine is highly automated vessel with a crew of only 32 officers and 58 enlisted submariners.
It is far quieter than previous Russian submarines and has a maximum “silent” speed of about 20 knots.
The U.S. Naval Institute’s Combat Fleets of the World said some reports suggest the vessel might have a maximum speed of between 35 and 40 knots. However, most Russian reports state a maximum speed of 35 knots. Like most new nuclear submarine designs, Severodvinsk’s reactor is designed to last for the life of the boat.
According the Office of Naval Intelligence (ONI), while the new Russian submarine is quieter than the Improved Los Angeles-class boats, the new vessel is not quite as silent as the Seawolf or Virginia-class. However, the Soviets were always only lagging slightly behind U.S. in quieting technology according to Navy sources. The Russians are already building improved versions of the Yasen design.
Unlike most Soviet submarine designs, the Yasen-class boats do not make use of a double-hull—instead it has hybrid design with a lighter structure over the vessel’s pressure hull according to Russia media reports.
Another unique feature for a Russian vessel is that it incorporates a spherical bow sonar called the Irtysh-Amfora for the first time. As a result, Severodvinsk has its torpedo tubes located at about mid-ship like U.S. submarines. The vessel has eight torpedo tubes, four of which are 650mm tubes while the rest are 533mm tubes. Combat Fleets of the World estimates that the Yasen-class might carry as many as 30 torpedoes.
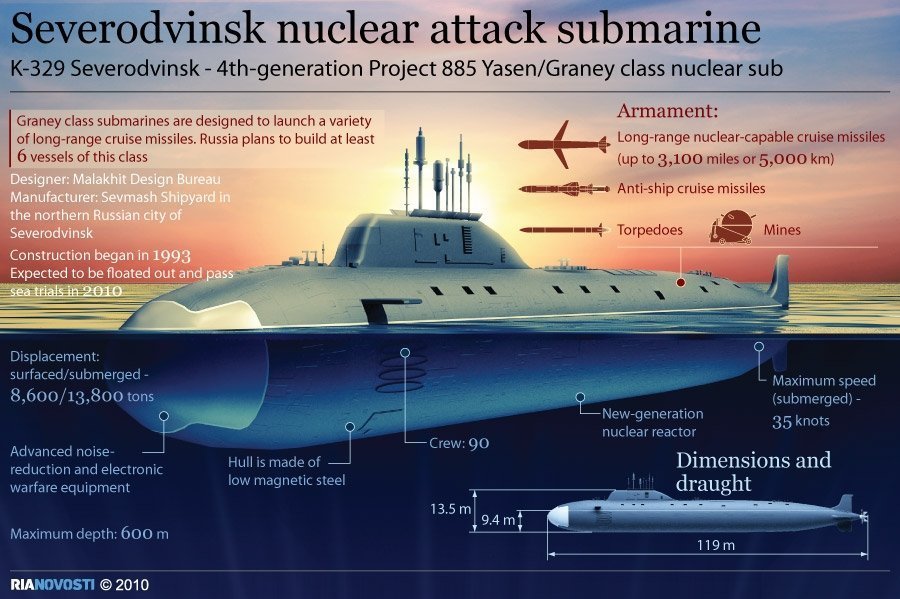
Like most Russian attack submarines, the vessel’s primary weapons are in the form of heavy anti-ship missiles. The boat has 24 missile tubes which can carry the supersonic NPO Mashinostroyeniya P-800 Oniks anti-ship missile which can hit targets roughly 200 nautical miles away. Severodvinsk can also carry Novator RK-55 Granat nuclear-capable 1,600 nautical mile-range subsonic land attack cruise missiles. Additionally, the Yasen-class boats can also launch the 3M14 Kalibr and 3M54 Biryuza land attack and anti-ship missiles, which have a roughly 300-mile range, though its torpedo tubes.
It also carries 91R anti-submarine missiles and has the capability to lay mines along with its normal complement of torpedoes.
Some Russian sources such as Russia Beyond the Headlines suggest that Severodvinsk is equipped with active anti-torpedo defenses and some sort of anti-air capability. The later would not be unprecedented, the Project 941 Akula—known better as the Typhoon-class ballistic missile submarine—was equipped with a 9K38 Igla surface-to-air missile system for ship self-defense.
Russia is expected to build eight Yasen-class boats. Since Severodvinsk took almost two decades to finish, the subsequent boats have many technological refinements to improve on the original Project 885 design. The next two Yasen-class boats are already under construction at the Sevmash shipyards in Severodvinsk, Russia. Kazan was laid down in July of 2009 while Novosibirsk was laid down July of 2013.